VITAMIN CHEAT SHEET & SIGNS OF MINERAL & NUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES
Vitamin Cheat Sheet
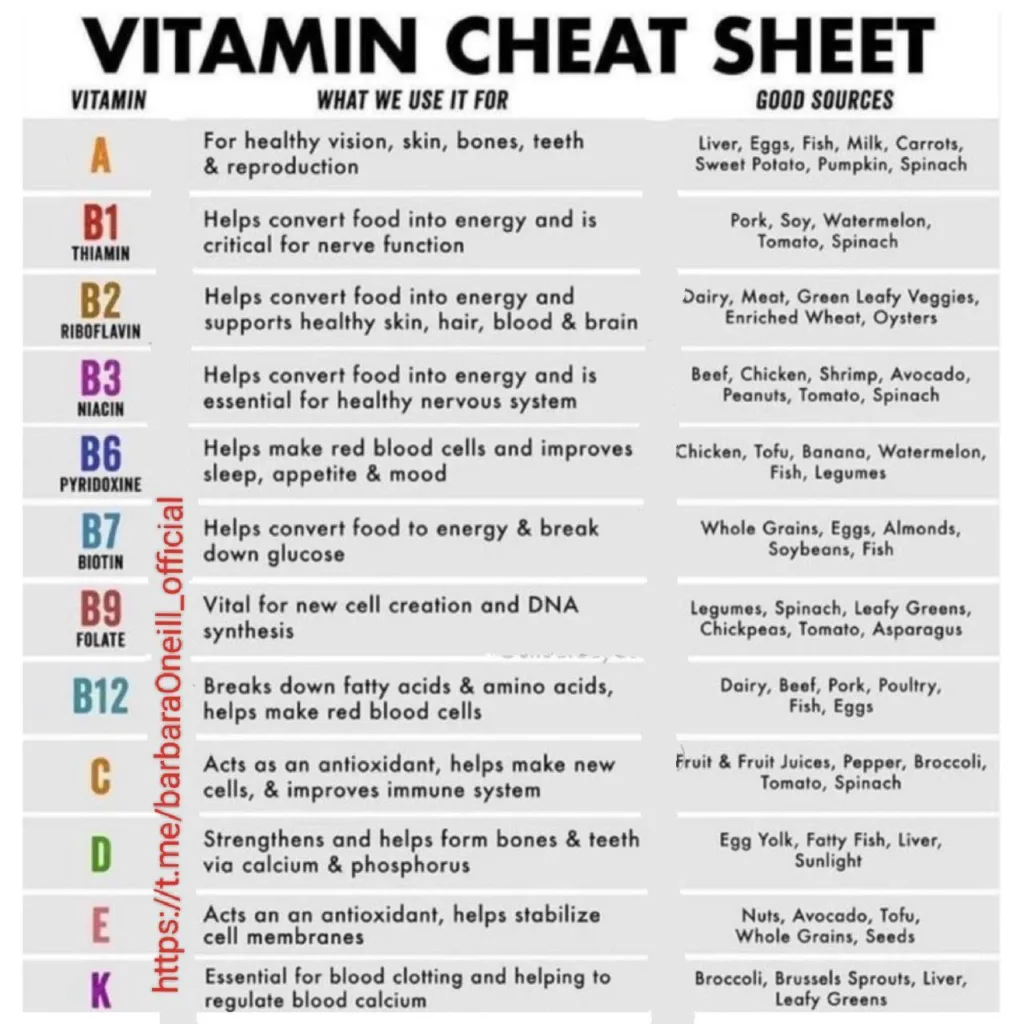
Vitamins are essential for maintaining health and well-being. Below is a comprehensive overview of the 13 essential vitamins, their functions, food sources, and signs of deficiencies.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
These vitamins are stored in the body’s fatty tissue and liver, and they include:
| Vitamin | Function | Food Sources | Deficiency Signs |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 (Thiamine) | Energy metabolism, nerve function | Whole grains, pork, legumes | Fatigue, irritability |
| B2 (Riboflavin) | Energy production, cell function | Dairy products, eggs, green leafy vegetables | Sore throat, cracks at mouth corners |
| B3 (Niacin) | Energy production, cholesterol management | Meat, fish, whole grains | Pellagra (diarrhea, dermatitis) |
| B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Hormone production, metabolism | Chicken, beef, potatoes | Rare; fatigue |
| B6 (Pyridoxine) | Amino acid metabolism, red blood cell production | Fish, poultry, potatoes | Anemia, depression |
| B7 (Biotin) | Fat and carbohydrate metabolism | Eggs, nuts, soybeans | Hair loss, skin rash |
| B9 (Folate) | DNA synthesis and repair; crucial during pregnancy | Leafy greens, legumes, fortified cereals | Neural tube defects in pregnancy; anemia |
| B12 (Cobalamin) | Nerve function; red blood cell formation | Meat, dairy products; fortified cereals for vegans | Anemia; neurological issues |
| C | Antioxidant; aids in iron absorption and immune function | Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers | Scurvy (bleeding gums) |
Signs of Deficiencies
- Vitamin A: Night blindness and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Vitamin D: Bone pain and muscle weakness.
- Vitamin E: Impaired vision and immune response.
- Vitamin K: Excessive bleeding or bruising.
- B Vitamins: Fatigue and neurological issues depending on the specific vitamin.
- Vitamin C: Bleeding gums and easy bruising.
Conclusion
A balanced diet rich in a variety of foods can help ensure adequate intake of these essential vitamins. If dietary sources are insufficient or if specific health conditions exist that affect absorption or needs (such as pregnancy or chronic illness), supplementation may be necessary. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.

